79. 单词搜索
Given an m x n grid of characters board and a string word, return true if word exists in the grid.
The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once.
Example 1:
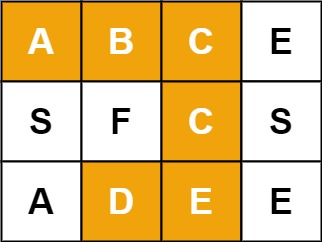
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED" Output: true
Example 2:
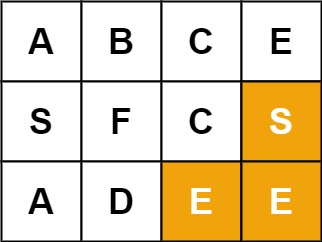
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE" Output: true
Example 3:
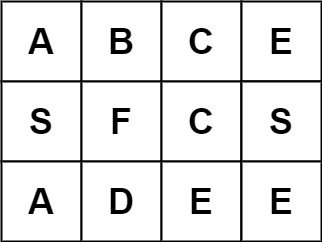
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB" Output: false
Constraints:
m == board.lengthn = board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 61 <= word.length <= 15boardandwordconsists of only lowercase and uppercase English letters.
Follow up: Could you use search pruning to make your solution faster with a larger board?
思路:
题目意思是给一个二维数组,给一个字符串,判断字符串是否在二维数组里面,标准的dfs题目,跟走迷宫的题目一样。对于二维数组的每一位,往上下左右四个放下探索,走过的路径用一个特殊字符标记一下就行,每找到单词中的一个字母,就结果加一,最终如果探索结果和单词长度相同,单词肯定就在二维数组里面。
代码:
golang:
func exist(board [][]byte, word string) bool {
var maxLen = 0
var words = []byte(word)
var maxMatch = math.MinInt32
for i := 0; i < len(board); i++ {
for j := 0; j < len(board[0]); j++ {
maxMatch = max(maxMatch, bfs(board, words, i, j, 0, maxLen))
if maxMatch == len(word) {
return true
}
}
}
return maxMatch == len(word)
}
var dests = [][]int{
[]int{-1, 0},
[]int{1, 0},
[]int{0, -1},
[]int{0, 1},
}
func bfs(board [][]byte, words []byte, i, j, idx int, maxLen int) int {
if i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= len(board) || j >= len(board[0]) {
return maxLen
}
if idx == len(words) {
return maxLen
}
if board[i][j] != words[idx] {
return maxLen
}
maxLen++
// 四个方向继续探索
maxMatch := maxLen
var nowMaxLen = 0
for _, dest := range dests {
nowVal := board[i][j]
board[i][j] = '-'
nowMaxLen = maxLen
idx++
maxMatch = max(maxMatch, bfs(board, words, i+dest[0], j+dest[1], idx, maxLen))
idx--
maxLen = nowMaxLen
board[i][j] = nowVal
}
return maxMatch
}
func max(i, j int) int {
if i > j {
return i
}
return j
}